Sodium citrate appears in many formulations across different industries. Its function is often assumed rather than examined, which can lead to confusion when selecting grades, forms, or application conditions.
Sodium citrate is a sodium salt of citric acid widely used as a buffering agent, chelating agent, and stabilizer in food, pharmaceutical, medical, industrial, and laboratory systems.
Sodium citrate is used in many fields for similar chemical reasons. Starting from its basic properties makes its broad application easier to understand.
What Is Sodium Citrate? Chemical Definition and Basic Characteristics?
The name sodium citrate[^1] sounds simple, but different forms and compositions can behave differently during formulation. A clear definition helps avoid practical misunderstandings.
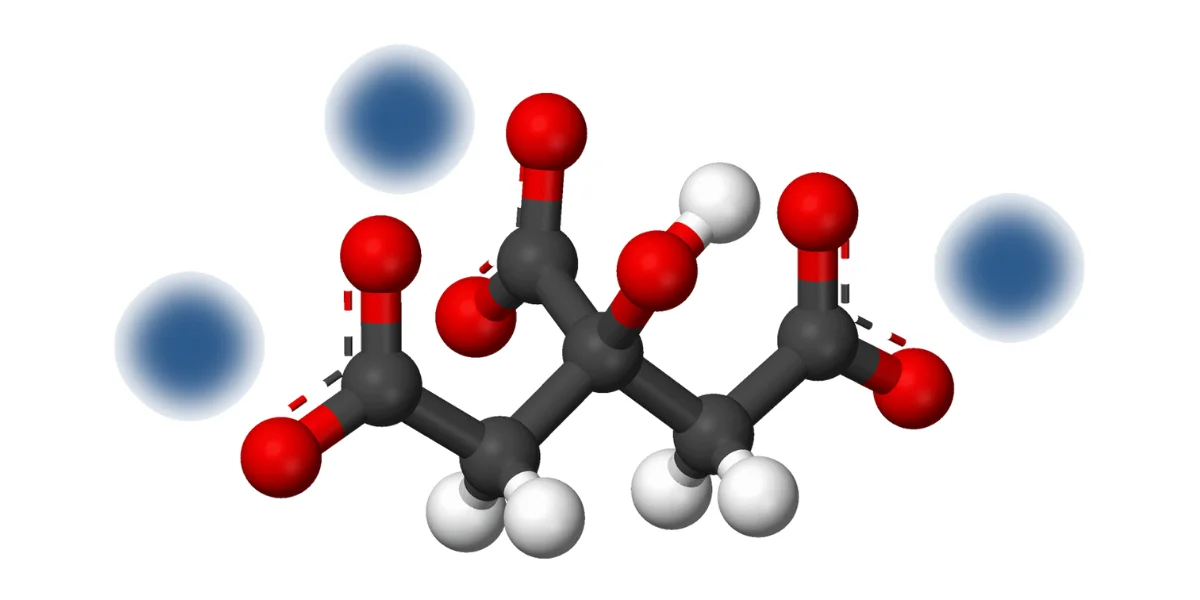
Sodium citrate is the sodium salt of citric acid, most commonly supplied as trisodium citrate[^2], with high water solubility and mild alkaline behavior.
Chemical identity and structure
In most commercial and industrial contexts, sodium citrate refers to trisodium citrate. It is produced by neutralizing citric acid with sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate. The commonly encountered chemical forms are:
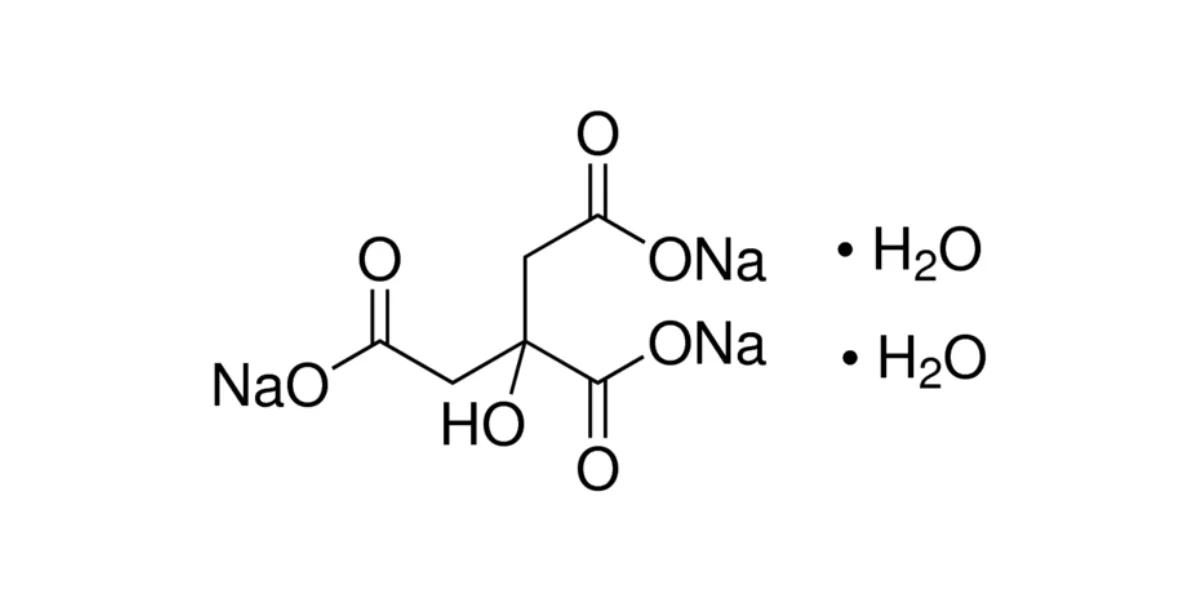
- Trisodium citrate (anhydrous): C₆H₅Na₃O₇
- Trisodium citrate dihydrate: C₆H₅Na₃O₇·2H₂O
The molecule contains three carboxylate groups, each associated with a sodium ion. This structure explains its ability to interact with hydrogen ions and metal cations.
Physical characteristics
From a handling perspective, sodium citrate shows consistent physical behavior across grades:
| Property | Typical Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White crystalline powder or granules |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Taste | Mildly saline |
| Solubility | Highly soluble in water |
| Stability | Stable under normal storage |
These characteristics make sodium citrate easy to dissolve, weigh, and blend in both liquid and dry systems.
General compatibility
Sodium citrate is compatible with many organic and inorganic substances. It does not easily oxidize and shows good stability across a wide temperature range, which supports its use in regulated environments.
How Sodium Citrate Works as a Buffer and Chelating Agent?
Many formulations depend on stable pH and controlled metal ion levels. Sodium citrate supports both through well-understood chemical behavior.
Sodium citrate helps maintain pH stability and binds certain metal ions, reducing variability in chemical and physical performance.
Buffering behavior
Citric acid is a weak acid with multiple dissociation steps. When combined with its sodium salt, the system resists rapid pH changes within a moderate range. This buffering action is commonly effective between pH 3 and 6.5.
In practical terms, buffering with sodium citrate allows formulations to:
- Remain stable when small amounts of acid or base are introduced
- Maintain consistent performance over time
- Reduce sensitivity to process variation
Chelation of metal ions
Sodium citrate can form complexes with metal ions such as calcium, magnesium, and iron. This chelation reduces the availability of free metal ions in solution.
The results often include:
- Less precipitation caused by calcium salts
- Improved clarity in liquids
- Reduced interference in chemical reactions
Combined effect in formulations
Buffering and chelation often work together. In many systems, sodium citrate stabilizes both pH and mineral balance, which explains its use as a multifunctional ingredient rather than a single-purpose additive.
What Is Sodium Citrate Used For in Food and Beverage Processing?
Food and beverage products are sensitive to changes in acidity, mineral content, and protein behavior. Sodium citrate is often selected to manage these factors in a controlled way.
In food and beverage processing, sodium citrate is used to regulate acidity, support emulsification, and improve product stability.
Acidity regulation
Compared with citric acid alone, sodium citrate provides smoother pH adjustment. It allows producers to fine-tune acidity without creating an overly sharp taste.
Typical applications include:
- Carbonated and non-carbonated beverages
- Powdered drink mixes
- Sauces and condiments
Emulsifying function in dairy systems
In processed cheese and related products, sodium citrate acts as an emulsifying salt. By binding calcium in milk proteins, it allows fats and proteins to form a uniform structure.
This leads to:
- Even melting behavior
- Consistent texture
- Reduced oil separation
Summary of food-related roles
| Application | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Beverages | pH control and flavor balance |
| Processed cheese | Emulsification |
| Confectionery | Stability and buffering |
| Ready meals | Shelf-life support |
Its ability to perform multiple functions helps simplify ingredient systems.
Uses of Sodium Citrate in Pharmaceutical and Medical Applications?
Pharmaceutical and medical products require consistent chemical conditions. Sodium citrate supports this consistency through predictable behavior.
In pharmaceutical and medical settings, sodium citrate is used as a buffer, excipient, and anticoagulant component.
Pharmaceutical formulations
Sodium citrate appears in various dosage forms, including:
- Oral liquids and syrups
- Effervescent preparations
- Injectable solutions
Its buffering capacity helps protect active ingredients from degradation and improves formulation stability.
Medical and clinical use
Because sodium citrate binds calcium ions, it is widely used as an anticoagulant in medical procedures such as:
- Blood collection and storage
- Apheresis treatments
- Dialysis systems
Citrate-based anticoagulation is valued for its controllability and reversibility.
Quality considerations
Medical and pharmaceutical grades of sodium citrate must meet strict purity requirements. Factors such as hydration state, particle size, and impurity profile can influence performance and must be clearly specified.
Industrial and Laboratory Applications of Sodium Citrate?
Sodium citrate is also used outside food and healthcare, particularly where pH and metal ion control are important.
In industrial and laboratory environments, sodium citrate supports reaction control, metal management, and analytical preparation.
Industrial processes
In chemical processing and surface treatment, sodium citrate is used to:
- Control metal ion availability
- Reduce unwanted precipitation
- Improve process consistency
It may appear in cleaning systems, surface treatments, and auxiliary formulations.
Laboratory use
In laboratories, sodium citrate is commonly used to:
- Prepare buffer solutions
- Stabilize enzymes and reagents
- Control ionic strength in experiments
Its predictable behavior supports standardized experimental protocols.
Typical application overview
| Area | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Chemical processing | Ion control |
| Cleaning formulations | Chelation |
| Analytical labs | Buffer preparation |
| Research | Reaction stability |
Anhydrous vs. Dihydrate Sodium Citrate: Key Differences Explained?
Different hydration forms affect handling and dosing. Selecting the correct form helps maintain formulation accuracy.
Anhydrous and dihydrate sodium citrate differ mainly in water content, molecular weight, and handling characteristics.
Structural differences
The dihydrate form contains two molecules of water bound within the crystal structure. This increases molecular weight and affects weight-based dosing.
Practical comparison
| Aspect | Anhydrous | Dihydrate |
|---|---|---|
| Water content | None | Present |
| Weight efficiency | Higher | Lower |
| Storage sensitivity | Lower | Slightly higher |
| Typical use | Dry systems | Liquid systems |
Application impact
Both forms provide the same chemical functionality. However, substituting one for the other without adjustment can affect concentration and performance.
Safety, Handling, and Regulatory Status of Sodium Citrate?
Sodium citrate is widely regarded as safe, but proper handling and documentation remain important.
Sodium citrate has a strong safety record and is approved for use across major regulatory frameworks when used as specified.
Safety profile
Sodium citrate is non-flammable, non-volatile, and shows low toxicity under normal conditions. Standard industrial hygiene practices are generally sufficient.
Regulatory acceptance
Sodium citrate is recognized and approved for use in food, pharmaceutical, and industrial applications in many regions. Specific purity and specification requirements depend on the intended use.
Storage and handling
Best practices include sealed containers, dry storage conditions, and clear labeling of grade and hydration state. Proper documentation supports regulatory compliance and supply chain transparency.
Conclusion
Sodium citrate is widely used because its buffering and chelating properties deliver consistent performance across food, medical, pharmaceutical, and industrial applications.
[^1]: Explore this link to understand the diverse applications and advantages of sodium citrate across multiple sectors.
[^2]: Discover the significance of trisodium citrate in food and pharmaceutical industries by visiting this informative resource.